Introduction
By: Mike Paladino - Revised: 2006-06-27 devinIntroduction
Learn about digital video, the advantages of digital camcorders, the history of video editing, and video standards and terms.Section Links
What is Digital Video?
All camcorders use one or more charged-coupled devices CCD. Personal camcorders usually have 1. Professional camcorders usually have 3. CCD’s are currently the device of choice for digital and consumer imaging devices like camcorders, scanners, and digital cameras.
The CCD is a light sensitive chip used for gathering the colored light information. An image sensor then converts the light coming through the lens into a digital signal. The digital signal is a series of electronic pulses based on the pattern of light that fell on the electronic sensor. The signal is then converted to the (1's and 0's) digital format that the camcorder uses.
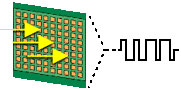
Most personal camcorders have 1 CCD to pick up the image and the colors.
Higher end professional camcorders have 3 CCD's. Each CCD picks up a different color, RED, GREEN, and BLUE. It then is combined via electronic circuit and has better color reproduction. The CCD has little sensors on it that pick up the image and convert it to a digital signal. These are usually referred as pixels. The more the better. Then the image and sound data are recorded onto the tape in the machine.
Digital vs. Analog
Digital data consists of nothing but 1's and 0's. It may be stored on similar physical material as analog data, but the recorder images are recorded as 0 and 1 and can be stored longer than analog tapes. The Digital data is usually converted back to analog data right before it is shown on the display of the playback device.Analog data uses a range of numbers such as 0 to 10000. There is a maximum and a minimum, but there is no limit to the number of in-between values.
Analog data storage is susceptible to data degradation and corruption. Over time, the data is changed because the physical material is imperfect. You can tell that it is corrupted when you see static, discolorations, or a blurry picture.
Digital Camcorder Advances
- Smallest Camcorders (size of a walkman)
- Smallest tapes
- Batteries last longer
- Quality better than analog
- Easy to transfer on a computer
- Recordings last longer
History of Video Editing
In 1990, the technology needed to create a movie cost $200,000.In 1995, the technology needed to create a movie cost $8,000.
Now, the technology needed to create a movie costs $1,500.
This is for an iMac (educational pricing) and a DV camcorder. It is possible to get these cheaper if one buys used, refurbished, or demo hardware.
Amazingly, the quality of this setup is far better than the quality of the $8,000 setup of 1995!!!
Video Standards and Terms
Video standards exist for TV's, TV stations, VCR's, VHS tapes, DVD players, DVD media, camcorders, and computer file format. The standard determines the number of frames per second and the pixel resolution.Frame
One image. When you take multiple images and display them one after another, you get "moving pictures".
Pixel resolution
The number of square or rectangle dots that make up an image.
Video Formats
Unless you intend on making VHS tapes to send to other countries, you don't need to worry about other video formats, other than to know that there are others. The three most commonly used are NTSC, PAL, & SECAM described below.
If you do need to use these formats, you will need to do a bit of research. Converting between one format and another is not something a beginner can just do. It might be better to hire or seek the advice of a professional.
- NTSC (National Television Standards Committee)
- NTSC is a video standard used in North and South America, Japan, and 30 other countries. TV's, VCR's, camcorders, and TV stations in these countries use this standard.
- 29.97 frames per second (fps)
- 720 x 480 rectangular pixel resolution
- 575 scan lines(the number of fine horizontal lines)
- PAL (Phase Alternating Line)
- PAL is the other main video format. This format is used in Europe, Africa, Middle East, Australia, China, and others.
- 25 frames per second
- 720 x 576 rectangular pixel resolution
- 625 scan lines (the number of fine horizontal lines)
- SECAM (SEquential Couleur Avec Memoire)
- SECAM is another video format used in France, the former Soviet Union countries, and others.
- 25 frames per second
- 720 x 576 rectangular pixel resolution
- 625 scan lines (the number of fine horizontal lines)
- Documentation
- Administration
- Authentication
- General Software
- Hardware
- Miscellaneous
- Multimedia
- Networking
- Operating Systems
- Outside Presentations
- Programming & Scripting
- Security
- Servers
- Short Courses
- System Deployment
- System Utilities
- What's New

